VMware vSphere 7: Managing and Configure vSwitch Networking

Why take this course?
It seems you're looking for comprehensive information on VMware vSphere 7 networking, specifically about the virtual switches (vSwitches) that are central to the virtualization environment provided by ESXi hosts within a vSphere setup.
Virtual Switches in VMware vSphere 7:
A virtual switch (vSwitch) is a key component of the VMware vSphere networking stack. It acts as a bridge between virtual machines and external networks, enabling them to communicate with each other and with physical network infrastructure. A vSwitch is implemented within an ESXi host and can be configured to serve various purposes, such as:
- Connecting Virtual Machines: Allows VMs to communicate internally or with external networks.
- Connecting Physical Networks: Enables the connection of physical network infrastructure for management traffic (like vCenter, iDRAC, ESXi console) and production workloads.
- vMotion: Facilitates the live migration of VMs between hosts without service interruption.
- Storage: Connects to storage systems like NAS or SAN for data storage and retrieval.
- Fault Tolerance: Supports FT logging network.
- High Availability: Supports HA heartbeat traffic.
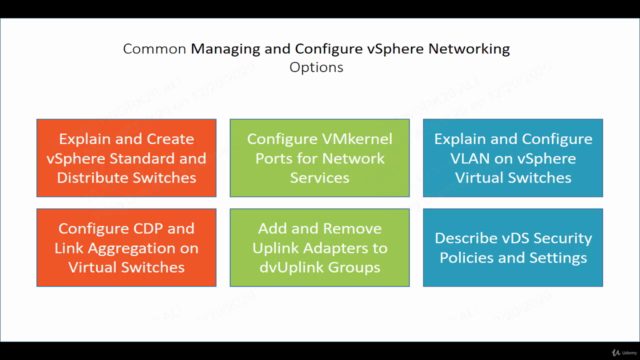
Types of vSwitches in vSphere 7:
- Virtual Standard Switch (vSS): A basic type of vSwitch suitable for most deployment scenarios, including production environments. It offers standard L2 networking capabilities and is used when high availability isn't required at the virtual switch level.
- Virtual Distributed Switch (vDS): Offers advanced features such as uplink failover, load balancing, and traffic shaping across multiple ESXi hosts within a vCenter environment. It's designed for larger environments where consistent management and high availability are critical.
Key Features of vSwitches:
- VLAN Configuration: Supports VLAN tagging and untagging to segment network traffic and enhance security.
- Security Policies: Applies security policies like port security, MAC address filtering, and promiscuous mode settings for network isolation and protection.
- Traffic Management: Includes features like Quality of Service (QoS), traffic shaping, and rate limiting to manage network performance.
- Network Policies: Enables the implementation of network policies that restrict network access between VMs or with external networks based on roles, security levels, or other criteria.
Installation and Configuration of vSwitches:
To install a vSwitch in vSphere 7, you would typically:
- Log in to your ESXi host or vCenter Server.
- Navigate to the network configuration section under the networking and security tab.
- Create a new vSwitch by specifying a name and configuring the necessary settings (e.g., VLAN IDs, mounting physical NICs).
- Connect virtual machines to the newly created vSwitch through their virtual network adapters.
- Configure additional settings like promiscuous mode, MAC address changes, etc., as needed.
Best Practices:
- Plan your network topology before creating vSwitches to ensure optimal performance and security.
- Use vDS for environments that require more robust management and failover capabilities.
- Regularly review and update the network policies and configurations to adapt to changing requirements or security threats.
Resources:
To get hands-on experience with VMware vSphere 7 networking, you can use the following resources:
- VMware vSphere Client: The web-based interface for managing your ESXi hosts and VMs.
- VMware Workstation or Player: For setting up and configuring vSwitches in a lab environment.
- Official VMware Documentation: Provides detailed guides and best practices for network configurations in vSphere environments.
- Online Courses and Labs: Offered by VMware or certified training partners to get certified (e.g., VCP-NV).
Remember that the specific steps and features may vary depending on the version of vSphere you are using, so always refer to the official documentation for the most accurate guidance.
Course Gallery


Loading charts...