Six Sigma: Lean Six Sigma Black Belt (Part 2) (Accredited)

Why take this course?
Based on the information provided, here is a structured outline of what you can expect in the Six Sigma Lean Black Belt (Part 3) course, focusing on Phases 2 and 3 of the Black Belt program:
Phase 2 - Measure
-
Introduction to Measure: Overview of the Measure phase, its importance in DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control), and how it fits into the overall project process.
-
Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ): Methods to calculate and analyze the costs associated with poor quality within a process, including prevention costs, appraisal costs, internal failure costs, and external failure costs.
-
Process Map: Techniques for mapping out processes to understand workflow and identify areas for improvement.
-
The 8 Wastes: Identification of the eight types of waste in a process that can lead to inefficiency, such as defects, overproduction, waiting, non-used talent, transportation, inventory, motion, and extra-processing.
-
Value Stream Map (VSM): A detailed analysis of the value stream of products or services for the purpose of optimizing operations.
-
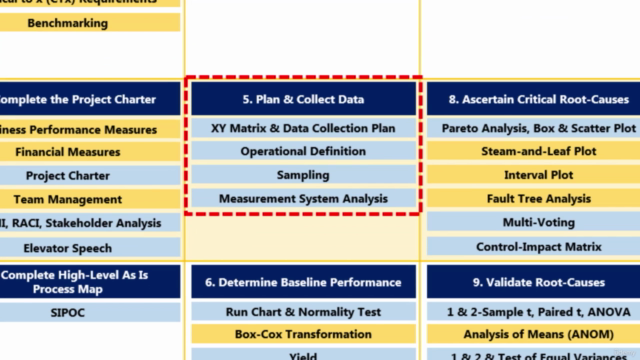
XY Matrix: A tool for understanding how different process inputs can affect outputs and for identifying which factors have the most impact on your process's performance.
-
Data Collection Plan: Strategies for systematically collecting quality data to measure a process's performance and to determine the nature of the variation in the process.
-
Operational Definition: Creating clear, specific definitions of terms used within a project so that everyone involved has the same understanding.
-
Sampling: Techniques for selecting samples from a larger population to make accurate assessments about the entire population without examining every individual element.
-
Measurement System Analysis (MSA): Evaluating the measurement system to ensure that it is capable of producing reliable data, focusing on errors and biases in the system.
-
Run Chart: A tool for monitoring a process over time to identify patterns or trends that can indicate stability or instability in the process.
-
Normality Test: Statistical tests used to determine if a set of data follows a normal distribution, which is critical for certain advanced statistical methods.
-
Box-Cox Transformation: A technique used to stabilize variances and transform data to achieve normality before applying advanced statistical techniques.
-
Yield: Calculating the yield of a process, which is the percentage of items that meet specifications after processing.
-
Process Capability - Discrete: Assessing the capability of a process with discrete data (counts or number of defectives) to meet customer requirements and expectations.
-
Process Capability - Continuous: Evaluating the capability of a continuous process to meet specific performance targets over time.
Phase 3 - Analyze
-
Introduction to Analyze: Understanding the purpose and importance of the Analyze phase in identifying root causes, underlying issues, and key factors that influence a process's performance.
-
Brainstorming: A technique for generating a list of potential solutions or root causes by systematically encouraging creativity from all participants.
-
Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa): A cause-and-effect diagram used to systematically identify and categorize the potential causes of a problem or a quality characteristic.
-
5 Whys Analysis: A technique to explore the root cause(s) of a problem by asking "Why?" five times, or as many times as necessary, alongside the corresponding "How?" to suggest potential solutions.
-
Pareto Analysis: Using the 80/20 rule to identify and prioritize the most significant factors that contribute to a problem or its solution.
-
Statistical Tools for Analyze: Introduction to various statistical tools, such as histograms, scatter diagrams, control charts, and process capability analysis, to analyze data and identify patterns or trends.
-
Root Cause Analysis: Techniques to drill down into the underlying reasons for problems, defects, or issues in a process to ensure that corrective actions address the true cause of concern.
-
Experimental Design: Planning experiments to test hypotheses about a process and to optimize it by determining the most significant factors affecting its performance.
-
Regression Analysis: Using statistical methods to examine relationships between variables, allowing for a deeper understanding of how changes in one variable might predict changes in another. Supplementary Materials:
- A set of 30 practice questions for Phase 2 and 3 to test your understanding and preparation for the Black Belt exam.
- Downloadable slides for Phase 2 and 3, which can be used as a reference or presentation aid.
This course is designed to equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to become a certified Six Sigma Black Belt and to apply these methodologies effectively in improving business processes. It is important to note that the actual certification process typically involves a combination of training, passing an exam, and applying the principles in real-world scenarios.
Course Gallery



Loading charts...