Physical Chemistry - Chemical Thermodynamics

Why take this course?
🚀 Physical Chemistry - Master Thermodynamics for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams! 🎓
Course Headline: Complete Chemistry for Engg and Medical Entrance Exam Preparation. (IIT JEE Main | Advanced | BITSAT | SAT | NEET etc.)
About the Course:
📚 Course Summary: Thermodynamics is the cornerstone of understanding energy transformations in chemical and physical systems. It quantitatively describes how energy changes within a system and between the system and its surroundings. By focusing on the system and its interactions with the environment, we can predict and calculate the heat (q) and work (w) involved in processes, using the first law of thermodynamics: ∆U = q + w.
🔬 Key Concepts:
- State Functions: Internal energy (∆U) is a state function, whereas heat (q) and work (w) are not. We follow conventions where q and w are positive when added to the system.
- Heat Capacity & Work: Heat absorbed or evolved is q = C∆T, and work can be measured by w = –pex ∆V for gases undergoing expansion.
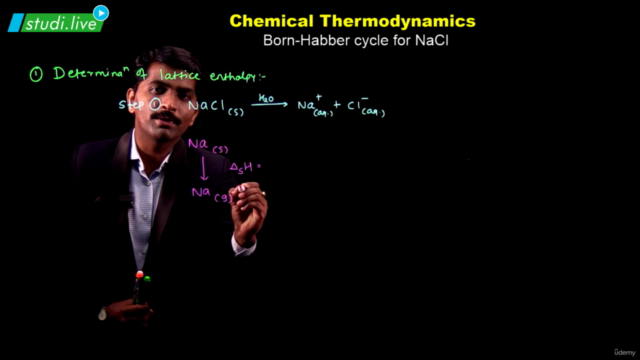
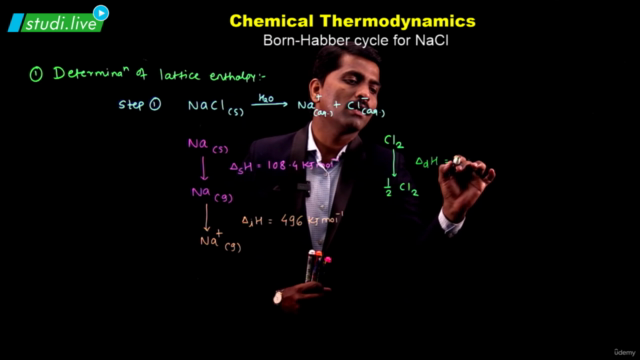
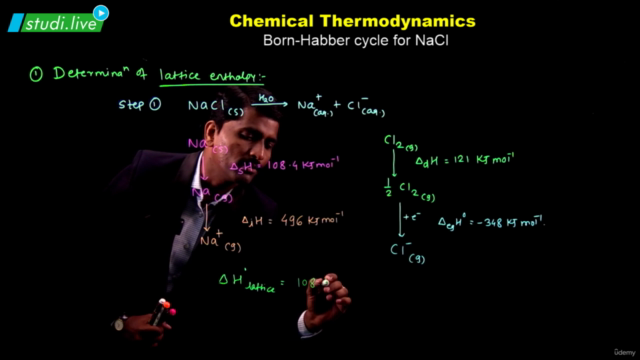
- Enthalpy: A state function introduced to handle chemical reactions at constant pressure, defined as ∆H = ∆U + ∆ngRT. Enthalpy changes during phase transitions (melting, vaporization, sublimation) and can be calculated using Hess's law.
- Entropy & Spontaneity: Entropy (S), a measure of disorder, indicates the spontaneity of a process in an isolated system. For such systems, ∆U = 0, and for spontaneous change, ∆S > 0 holds true.
- Reversible Processes: The quantity qrev/T, independent of path, determines the entropy change during a reversible process.
🧐 Challenge Yourself with Practice Questions:
- Identify which thermodynamic state function is used to determine heat changes and its value at equilibrium.
- Determine the condition for a process to occur adiabatically.
- Understand how enthalpies of elements in their standard states are defined.
- Calculate the enthalpy of formation of methane (CH₄) using combustion enthalpies of its elements.
- Assess whether a reaction will be possible at different temperatures based on its entropy change.
- Compute the change in internal energy for a process involving heat absorption and work done by the system.
- Calculate the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of aluminium under specific conditions.
- Determine the heat released during the formation of carbon dioxide (CO₂) from carbon and oxygen gas.
- Find the enthalpy change for a reaction involving CO, CO₂, N₂O, and N₂O₄ using their enthalpies of formation.
- For an isolated system where ∆U = 0, calculate the change in entropy (∆S).
- Determine the temperature at which a reaction will become spontaneous when ∆H and ∆S are constant over a range of temperatures.
- Analyze the signs of ∆H and ∆S for the reaction of chlorine gas into diatomic chlorine.
📈 Real-World Application: Mastering thermodynamics is essential for tackling entrance examinations for engineering and medical programs, where it forms a crucial part of the syllabus. This course will not only help you understand the concepts but also apply them to solve complex problems, giving you a competitive edge.
👩🏫 Your Expert Instructor: Learn from an experienced educator who has a knack for breaking down complex principles into digestible lessons, ensuring you have a solid grasp of the material before moving on to more advanced topics.
🚀 Enroll Now and Elevate Your Understanding of Thermodynamics! 🎯 Don't miss out on this opportunity to excel in your upcoming exams with a deep dive into thermodynamics. Sign up today and secure your spot among the top scorers!
Course Gallery

Loading charts...