Global Warming and it's related concepts in Hindi
Details of Green house gases & it's related concepts.
4.81 (8 reviews)

66
students
2 hours
content
Nov 2022
last update
$29.99
regular price
Why take this course?
based on the information provided, here's a summary of the obligations and mechanisms under the Kyoto Protocol, as well as other environmental issues like acid rain, deforestation, biodiversity loss, ozone depletion, and coastal zone regulations:
Kyoto Protocol Obligations and Mechanisms:
- Energy Efficiency: Enhance to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- Carbon Sinks and Reservoirs: Protect and enhance to store GHGs.
- Sustainable Land Use: Promote sustainable forest management, afforestation, reforestation, and sustainable agriculture practices.
- Renewable Energy: Research, promote the development, and increase the use of new and renewable forms of energy.
- CO2 Sequestration: Encourage technologies to capture and store CO2.
- Fiscal Incentives: Phase out subsidies that encourage GHG emissions.
- Transport Sector: Promote measures to limit or reduce GHG emissions.
- Methane Emissions: Limit or reduce emissions from waste management, energy production and transport, as well as from aviation (bunker fuels) and marine bunker fuels.
- International Cooperation: Work together with other parties of the protocol to address climate change.
Specific Kyoto Protocol Commitments:
- Reduction Targets: Industrialized countries (Annex I) committed to reducing their GHG emissions by an average of 5.2% below 1990 levels during the first commitment period (2008-2012).
- Progress by 2005: Countries were expected to make demonstrable progress towards their commitments.
- Transition Economies: Flexibility for countries undergoing the process of transition to a market economy.
Mechanisms:
- Joint Implementation (JI): Allows Annex I parties to implement project activities in countries that are not members of the European Community or USA, and use the emissions reductions towards their own commitments under the Kyoto Protocol.
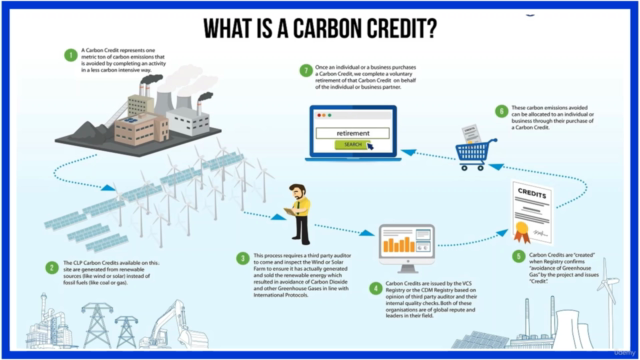
- Clean Development Mechanism (CDM): Enables emission-reduction projects in developing countries to earn certified emission reduction credits, which can be counted towards developed countries' greenhouse gas reduction targets.
- Carbon Trading: Parties can trade emissions allowances, providing economic incentives for reducing GHG emissions.
Acid Rain:
- Formation: Sulfur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) are emitted into the atmosphere and transformed into acids that can fall as acid rain or dry deposition.
Deforestation:
- Consequences: Loss of biodiversity, soil erosion, changes in water cycles, reduced capacity to store carbon, and habitat destruction for indigenous peoples.
Biodiversity Loss:
- Impact: Reduction in variety of plant and animal species, which can lead to disruptions in ecosystems, food chains, and human health.
Ozone Depletion:
- Chemicals: Ozone layer depleting substances (CFCs, halons, etc.) have been banned or restricted due to their harmful effects on the ozone layer.
Coastal Zone Regulations:
- CRZ Rules in India: Regulate activities within the coastal region to protect biodiversity and natural resources. The no-development zone has been set at 20 meters for certain islands and backwater areas.
These measures are critical in addressing environmental issues and ensuring sustainable development. The Kyoto Protocol, through its mechanisms like JI, CDM, and carbon trading, aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and provide financial incentives for cleaner technologies. The protection of natural ecosystems such as forests and coastal zones is also paramount for the health of our planet and the well-being of all its inhabitants.
Course Gallery

Loading charts...
Related Topics
4396588
udemy ID
14/11/2021
course created date
22/11/2021
course indexed date
Bot
course submited by