Carrier peering : SIP and ENUM protocol

Why take this course?
- "IP-NNI (Network-to-Network Interface) Security" presents a comprehensive overview of the security considerations, mechanisms, and best practices for implementing and managing an IP-NNI in a telecommunications network. This document is intended for network operators, solution designers, and anyone involved in the deployment or management of IP-NNI connections.
The content is structured into several key sections:
Part I: Introduction to IP-NNI
This section covers the basics of NNI, its importance in the telecommunications ecosystem, and how it differs from traditional network interfaces. It also introduces the concept of IP-NNI and its role in facilitating direct interconnection between IP networks.
Part II: ENUM
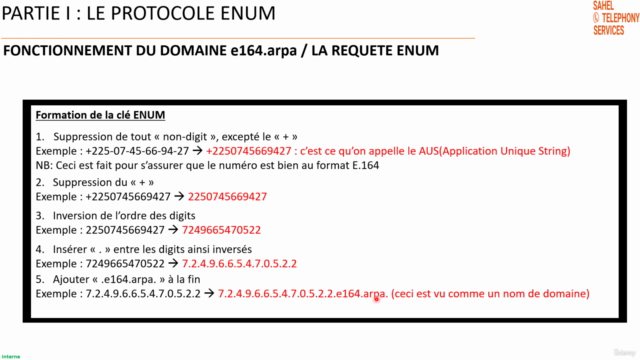
ENUM is a global distributed directory infrastructure that enables services like phone number lookup to be performed over the internet using DNS and other protocols. This part delves into the technical details of ENUM, including:
- ENUM service overview
- ENUM domain registration process
- ENUM query flow and response formats (NAPTR records, ENR records, etc.)
- ENUM types (Public ENUM, Private ENUM, Carrier ENUM)
- Security considerations for different ENUM types
Part III: Peering and Interconnect (VoIP and Video)
This section discusses the peering arrangements between service providers, including:
- Billing and settlement considerations
- Multi-lateral peering arrangements and their impact on interconnection
- Return to ENUM processes for handling calls from PSTN networks
Part IV: IP-NNI Architecture and Security Mechanisms
Here, the document outlines the architecture of an IP-NNI, including the layers involved (routing, protocol, and transport) and the security mechanisms that can be applied at each layer. It also covers:
- The importance of trust models in IP-NNI
- Identity management within IP-NNI
- Handling PSTN numbers and their integration with IP networks
- Use of SIP headers like P-Awareness-of-Early-Media (PAEM) for early media handling
- Portability aspects, call forwarding, and routing considerations
- Troubleshooting methods, including SIP options and overload control mechanisms
Part V: IP-NNI Routing Considerations
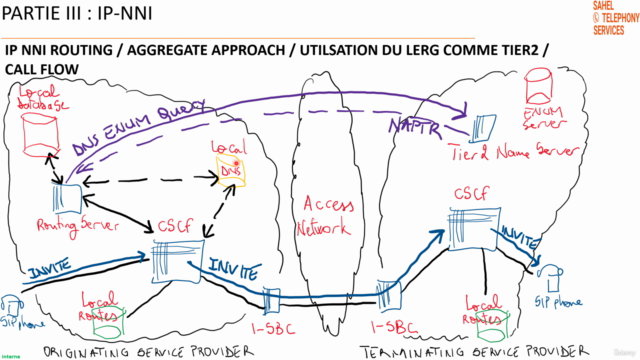
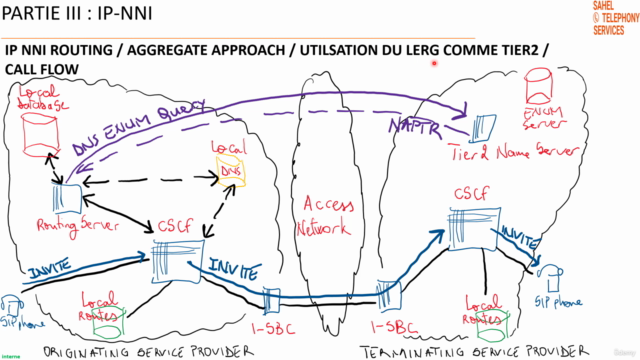
This section provides an in-depth look at the various routing strategies for IP-NNI, including:
- Detailed explanation of per-TN (Telephone Number) and aggregate approaches to routing
- Utilization of LERG (Location Exchange Routing) and NPAC (Number Portability Administration Center) databases in routing decisions
- Call flow diagrams and explanations for both IP-to-IP and IP-to-PSTN scenarios
- Security considerations and best practices for each approach
Part VI: Advanced Topics on IP-NNI Routing
In this final part, the document explores advanced routing concepts, including:
- The role of Tier 0/1 independent ENUM registries in routing decisions
- Security implications and mitigation strategies for ENUM registries at different tiers
- Case studies and real-world applications of IP-NNI routing strategies
Overall, "IP-NNI (Network-to-Network Interface) Security" provides a detailed guide to understanding and implementing secure IP-NNI connections. It emphasizes the importance of interoperability, security, and reliability in modern telecommunications networks and offers practical advice for network operators navigating this complex landscape.
Course Gallery

Loading charts...