A simple road-map to Energy, Rate and Reversible Reaction

Why take this course?
🌟 Unlocking the Essentials: Mastering Energy, Rate, and Reversible Reaction 🌟
Energy in Chemistry
Understanding energy is fundamental to chemistry. This course begins with an Introduction to energy and provides practical examples that illustrate how energy is conserved and transformed during chemical reactions. We'll explore:
-
Energy Involvement During Physical and Chemical Changes: Learn how to identify where energy comes into and goes out of a system, distinguishing between the system and its surroundings.
-
Exothermic vs Endothermic Reactions: Gain insights into reactions that release (exothermic) or absorb (endothermic) heat. We'll visualize these temperature changes through graphical representations, making it easier to grasp the concepts.
-
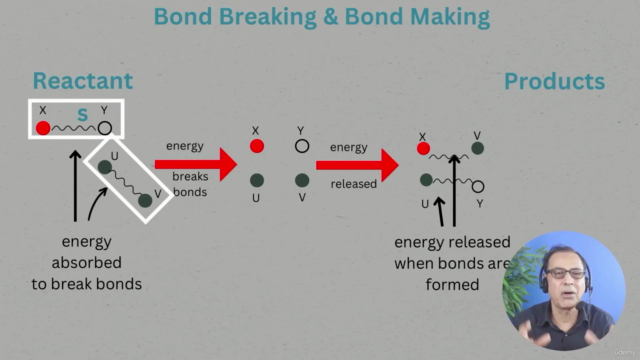
Energy Changes During Bond Making and Breaking: Through diagrams and real-life examples, understand how energy is associated with forming and breaking chemical bonds.
-
Energy Profile Diagrams: Examine detailed diagrams for both exothermic and endothermic reactions to visualize the energy landscape of a reaction.
Rate of Reaction
Rates are the heartbeat of chemistry. This section covers:
-
Introduction and Definition of Rate: Begin with the basics, understanding what rates of reaction are and how they're measured.
-
Collision Theory: Dive deep into the core concept that explains why reactions occur at specific rates. Learn about unsuccessful collisions and the importance of successful collisions, activation energy, and proper orientation of particles.
-
Factors Affecting Rate of Reaction: Explore how factors like concentration, temperature, surface area, catalysts, and pressure influence reaction rates, with graphical representations for each concept to solidify your understanding.
-
Measuring Rate of Reaction: Discover various methods to measure the rate at which reactions proceed, from monitoring gas production to detecting changes in color or mass loss in solids.
Reversible Reactions
Not all reactions are one-way streets. This section delves into:
-
Dynamic Chemical Equilibrium: Understand the concept of reversible reactions and how they reach a balance point between reactants and products, with real-life examples including Anhydrous CuSO4 into hydrated CuSO4 and Anhydrous CoCl2 to Hydrated CoCl2.
-
Le Chatelier's Principle: Learn how to apply this fundamental concept to predict the effect of changes in concentration, temperature, and pressure on the position of equilibrium.
Haber Process
The Haber process is a critical industrial method for synthesizing ammonia. We'll cover:
-
Raw Material and Conditions: Explore how pressure and temperature optimize the yield of ammonia in the Haber process.
-
Uses of NH3: Discuss the various applications of ammonia, from fertilizers to explosives.
Contact Process
Another pivotal industrial process, the contact process is essential for converting sulfur dioxide into sulfuric acid. We'll examine:
-
Raw Material and Process: Learn about the materials involved and the step-by-step process of the contact method.
-
Uses of SO2 and H2SO4: Explore the myriad uses of sulfuric acid, a key component in many industrial processes.
Past Paper Review & Solution
This section is crafted to provide O-Level students with valuable insights, helping them effectively tackle past paper questions. Through meticulous review and step-by-step solutions, you'll gain a deeper understanding of the material and be better prepared for your exams.
Join us on this enlightening journey through the world of chemical reactions, where energy, rates, and reversibility become clear. With this comprehensive guide, you'll master the concepts that will lead to success in your chemistry studies! 🎓✨
Course Gallery



Loading charts...