5G Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) & Optimization

Why take this course?
5G mobility optimization is a critical aspect of network performance, ensuring high-quality service for users as they move around the network. In this context, we'll delve into various aspects related to 5G mobility optimization, particularly focusing on A3 and A5 events, handover procedures in both NSA (Non-Standalone) 3X and 5G SA (Standalone), dynamic anchor point selection handover, and neighbor list optimization.
Section 4: 5G Mobility Optimization
Introduction to 5G Mobility Optimization
Mobility management in 5G networks is more complex due to the high data rates, large bandwidths, and massive device connectivity. Efficient mobility management is crucial for maintaining continuous service as users move across different cell areas or between different types of networks (NSA and SA).
Understanding A3 Events
A3 events in 5G refer to a neighbor cell being measured by the UE with RRC connection established when the Radio Resource Management (RRM) measurement reporting condition is satisfied. These measurements are essential for triggering handovers, which allows for seamless connectivity as the UE moves. Analyzing A3 measurements can help in optimizing the Radio Network Temporary Identifier (RNTI)-based measurement configuration and the measurement report configuration to reduce the number of unnecessary measurements and reports, thus optimizing the network performance.
Understanding A5 Events
A5 events occur when a UE with an RRC connection established performs measurements on neighbor cells under RRM measurement reporting conditions that are not satisfied, typically due to measurement configuration errors or as part of periodic measurement reports. Optimizing A5 events involves ensuring the correct configuration of the measurement configurations and preventing excessive signaling overhead associated with unnecessary measurements.
PSCell Change (Handover) Procedure in NSA 3X
In NSA 3X, the handover process involves several steps, including:
- Measurement reports from the UE (A3/A5 events).
- Analysis of these reports by the Mobility Management Entity (MME) or Access Gateway (AGW).
- Decision making for handover initiation.
- Sending the handover command to the UE.
- The UE performing the handover to the new cell, which may involve a change in the gNodeB (gNB).
Inter-gNB Handover Procedure in 5G SA
In a 5G SA network, the handover process is more streamlined due to the absence of an MME or AGW. The procedures include:
- Measurement and reporting by the UE (A3/A5 events).
- Decision making for handover initiation at the core network (CN) or by the gNB itself using the Session Management Function (SMF).
- Sending the handover command directly to the UE.
- The UE performing the handover to the new cell, possibly within the same gNB or between different gNBs.
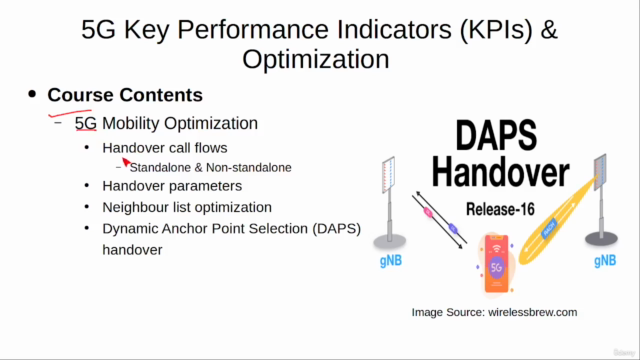
Dynamic Anchor Point Selection Handover
Dynamic anchor point selection handover is a technique where the network dynamically selects an anchor point for the session during handover. This can optimize the handover by reducing the potential for packet loss and improving the overall user experience.
Neighbor List Optimization
Optimizing the neighbor list involves configuring the correct set of neighbor cells for each cell. This includes setting up the appropriate RNTI values and ensuring that the neighbor list is accurate to minimize unnecessary handover attempts and optimize radio resource management.
By carefully managing these aspects of 5G mobility optimization, network operators can improve the user experience by minimizing dropped calls, reducing latency, and enhancing throughput during handover events. Proper configuration and monitoring of the network parameters related to mobility management are essential for achieving optimal performance in a 5G environment.
Course Gallery
Loading charts...